This tutorial describes how a 555 timer can be used to clock a binary counter, which is then shown on a seven segment LED display. The parts are connected such that only numbers 1 to 6 are used, resulting in an electronic dice application.
Overview
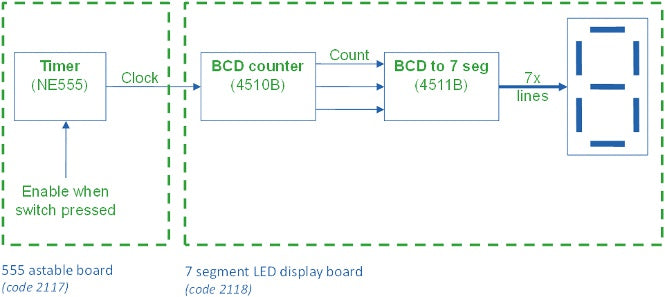
The basic block diagram is shown below:

On the left of the diagram is a 555 timer IC. When the switch is pressed this is held out of the reset state and begins to generate a square wave clock signal. This signal changes many times each second and is used to clock a binary coded decimal counter. The counter is setup so that it counts down from six until it reaches zero. At zero the counter is reloaded with the value six. This cycling through the numbers continues whilst the button is pressed and the clock from the timer is present. As soon as the button is released the counting stops, at this point whatever number the counter is on is where it stays. The final stage in the process is to convert the binary number into an output which can be shown on the 7 segment display.
Parts List:
- 555 astable timer kit (stock code 2117)
- 7 Segment LED display kit (stock code 2118)
555 Timer
The 555 astable board uses a 555 timer in its astable configuration. This means that it outputs a square wave or a series of high and low signals. The speed that the signal goes high and low is set by the capacitor C1 and variable resistor R3. The board is designed to make a tone so will be switching quickly on and off which is just what’s required for the 7 segment dice. The purpose of the 555 timer is to generate a clock signal whenever the switch is pressed. When this happens the 7 segment will be clocked through the various numbers. The circuit diagram of the 555 astable circuit is shown below:

Counter
The counter selected is a binary coded decimal four bit up down counter (4510B). This means that it can either count up from zero to nine or down from 9 to 0 and that the output of this is indicated in binary.

The diagram above shows how the counter operates when clocked, the solid line indicating a clock when set to up and the dotted line shows the step when clocked in the down mode. The second number in each of the boxes is the binary representation of the data that will be present on the counter outputs Q3 to Q0.
The chip has a Terminal Count (TC) output, this is normally present to allow one counter to trigger another counter when the count wraps around. This pin can however be used to reset the counter itself. The pin is active low so will be low: if counting up – when it reaches nine or if counting down – when it reaches zero.
The chip also has a Parallel Load (PL) function. When the PL pin is taken high the data on the inputs P3 to P0 are loaded into the counter. This functionality can be used to reload the counter with any value. So it is possible to load six and count down. When zero is reached the TC pin will change from high to low and this can be used to reload the counter to six.
Unfortunately the PL pin is active high and the TC pin is active low, so they can’t be connected directly. Instead an NPN transistor and pull up resistor need to be used to invert the signal.
The following table lists the pins not mentioned so far and their setting:
| Pin name | Description | Connection |
| CE | Count Enable (active low) Low = Counting functionality enabled High = Clocking the count line has no effect, the previous value is held |
Low |
| CP | Clock in – causes the count to either go up or down by one | To the 555 timer output |
| UP / DN | Up / Down Mode Low = down High = up |
Low |
| MR | Master Reset (active high) Low = normal operation High = hold the device in a reset state, where CP, PL and outputs Q3 to Q3 are disabled |
Low |

7 Segment converter
The final step in the process is to turn the binary encoded number into outputs that can drive a seven segment display. This is done with a BCD to seven segment converter IC, specifically the 4511B. This part has four input lines in BCD format and 7 output lines to drive the seven segments on the number. A few extra control lines are present as follows:
| Pin name | Description | Connection |
| LT | Lamp Test (active) Low = Turns all segments on, for test purposes High = Normal operation |
High |
| BI | Blanking (active low) Low = turns all segments off High = displays the required number The blanking pin can be used with a high speed variable width square wave to provide a dimming function |
High |
| LE | Latch Enable Low = Normal operation High = previously displayed number is latched and held |
Low |
The final step is to connect the seven segment display to the IC. To do this a current limit resistor is required and a 330 Ohm will give a good brightness.
Connecting the boards
The following diagram shows how the Kitronik 555 astable board should be connected to the 7 segment display board:

Download a pdf version of this page here.
Learn more about the author read more »